A Naunced View on Web3
Posted on March 6, 2022 • 8 minutes • 1538 words
As I reflected on my journey into tech, I realized that my motivations and interests are linked to liberation. Liberation is why I studied the Civil Rights Movement, why I was interested in history, and why I got into cybersecurity and tech. I have been in plenty of Web3 Twitter spaces over the last couple of weeks, and I often hear that Web3 is revolutionary because it has the potential to liberate people. So I am asking the question: what is Web3 and how does it liberate people?
Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs are under the umbrella of web3, or Web 3.0. It is helpful to consider the history of the web to understand how Web3 works. There is no defining moment where Web 1.0 turned into Web 2.0 turned into Web 3.0.
Web 1.0 was the first iteration of the web that was composed of static HTML pages. This means that all you could do was load the page and read its contents. The picture below shows an example of what a website in Web 1.0 looked like.
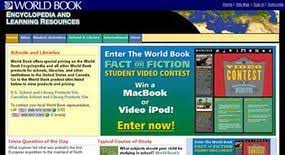
Web 2.0 is the current iteration of the internet as we know it. Unlike Web 1.0, it allowed content creators and its users more participation. It let people comment on websites and blogs and allowed more people to share content online. This helped power sites like Youtube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Web3, or as I like to refer to it as Web2+, refers to a movement towards decentralization of power from entities that control the internet. In the current iteration of Web2.0, social media sites like Facebook, Google, Twitter control user data and users are dependent on the platform. A problem in Web2.0 is that content creators rely on the algorithm to make sure that their content is shared, and for content creators to make money, the platform needs to be up and running. Although sites like Instagram are usually accessible, there have been times where Instagram has been down that would affect your income as a creator (Imagine if you were promoting a product live and the Instagram site was down). Users also do not control how these companies store and use their data. Web3 attempts to take power back from these companies through decentralization.
How does Web3 decentralize?
Web3 tries to decentralize the web through technology, specifically, the blockchain. This technology drives cryptocurrencies and everything else in the Web3 space. Blockchain is a public database that is managed by computers across the internet that stores transaction history. For a transaction to go through, it has to be verified by each computer on the network, making it more transparent, reliable, and resilient. Since many computers in the blockchain network have to verify the transaction, it is almost impossible to modify it once the transaction has been completed. Another advantage of blockchain technology is that it is public and allows others to view the transaction history.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are virtual currencies underpinned by cryptographic systems. They enable secure online payments without the use of third-party middlemen. “Crypto” refers to the various encryption algorithms and cryptographic techniques that safeguard these entries. There are many different types of cryptocurrencies and each type of cryptocurrency tackles different problems. Bitcoin The first major cryptocurrency developed was by Satoshi Nakamoto and is a pseudonym used by its founder or group of founders. Bitcoin is created, traded, and stored on a public ledger, the blockchain, and stores value. The difference between Bitcoin and other traditional currencies like the dollar is that it is not backed by an institution such a bank or a government and has a fixed amount of bitcoin.
Ethereum and smart contracts
Etherum is the second most popular cryptocurrency behind Bitcoin and is considered a second generation cryptocurrency. Just like Bitcoin, it stores value and can be used as a token for commerce. The biggest difference between Etherum and Bitcoin is that Ethereum has smart contracts capability as a second-generation cryptocurrency. A smart contract is code that runs when certain criteria are met and runs on the blockchain. The use of smart contracts could have many use cases in the business world. Its potential lies in giving power back to the individual by removing the intermediaries.
For example, to send remittances from Country X to Country Z, a middleman, an institution of some sort, usually gets a percentage of the remittance, and verifying the transaction can take time. By using a second-generation cryptocurrency that enables smart contracts, the middleman is removed, the transaction verification can go faster, and it allows the individual to keep a higher percentage of their earnings.
Another use case for using smart contracts is in the supply chain industry. To send products, wherever it is, medical supplies, food, or anything else, there are many points in which the product can be compromised. Currently, the only way to see if a product has been compromised is if the consumer reports the problem. To sort this issue, we guess where the product may have gotten compromised in the supply chain (that is right, the best way we solve this problem is guessing. Having a proper audit process in a complex supply chain is painful). The use of blockchain and smart contracts can improve this process because it will meticulously record each step of the supply chain and at each point of the supply chain, vendors will be able to verify the condition of their product.
The two examples above are a few examples of how technologies in the Web3 ecosystem can improve our current system processes. This technology is still new, there will be many more opportunities for various industries, and businesses to plug into the different technologies that underpin Web3. However, for the same reason, there are HUGE problems that have yet to be addressed, and many technologies are still a work in progress.
One of the biggest problems in this space is the lack of defined infrastructure. Web3 architecture is still in its primitive stages. Before the pandemic, the people who knew about Web3 were mostly in tech or in online communities. However, when the pandemic hit, more people and institutions flooded towards Web3 and saw it as an opportunity to make money. The Web3 infrastructure was not ready for this mass adaptation. Like any great city, it takes time to build the roads for the cars to drive on, it takes time to make the houses for people to live in, and it takes time to make a sewage system. Just like London in the 1900s, or a new city that grew exponentially in a short time, Web3 is experiencing significant growing challenges.
The biggest concern with the lack of defined infrastructure leads to significant security concerns. With so many paradigm shifts, new protocol designs and redesigns, and the pressure to be first to market, attack surfaces have increased, and developers have not been able to keep up. It is like having to referee a game (a soccer, or NBA game), but the rules of the game changes in live time. The referees will do the best they can, but it is nearly impossible for them to enforce the laws before they understand them. Even if the referees understand the rule changes, inevitably, they will miss the call in the previous play that was legal just moments ago. Not only that, the referees will have to determine how far to pull the play back in a major moment, and there will be players that use this confusion to their advantage. The referees will also have to explain each significant decision to the players, coaches, and fans to understand and enjoy the game.
The developers in Web3 space are like the referees in this space and at times put in impossible situations. Their job will only get easier when a consensus is reached between all parties and the rules are agreed upon.
My answer to the question does Web3 liberate people is that it depends. To those who live in countries where inflation is rampant, cryptocurrencies give an alternative currency for people to hold value. I am thrilled that artists can sell their work as NFT’s and generate lots of money to change lives. But if the basic idea behind Web3 is about sharing and including more people in the decision-making process, then this idea is not new. Christianity, communism, democracy, these were all conceptions that tried to incorporate ideas of sharing into the mainstream and were considered revolutionary at a point in time. In the end, technology is only a medium in which ideas are expressed, and technology is a microphone that magnifies strengths and weaknesses.
My hope for Web3 is that it enables more people worldwide to participate in the global economy that allows us to lift more people out of poverty. I hope cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ada, and others will empower more people to build better futures. However, while there is enormous potential for Web3, I also know from history that no technological revolution can solve the human problems of classism and racism. My ultimate hope is that the builders, creators, policymakers, consumers, Web3 enthusiasts, and Web3 skeptics will all work together to form a better future, whether it is in the Web3.0 space or not.

